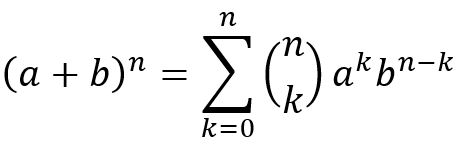Stable Isotopes - Abundances %
The key elements in organic chemistry are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), phosphorus (P), sulfur (S), chlorine (Cl), and bromine (Br). These elements naturally occur as mixtures of isotopes, which significantly influence the isotope distribution. Isotopes are atom species of the same chemical element that differ in mass. They have varying numbers of neutrons, while the number of protons and electrons remains the same.
Contact us for stable isotope synthesis
Isotope peak intensities
Molecules with n halogen
The formula used has the form of: |
|
 | ||||
| (a + b)2 = a2 + 2 a b + b2 where a = percentage of 35Cl and b = percentage of 37Cl. | Intensities | |||
| 35Cl2 | m | (75.76 2) | 57.4 | 100 |
| 2 (35Cl 37Cl) | m+2 | (2 x 75.76 x 24.24) | 36.7 | 64 |
| 37Cl2 | m+4 | (24.242) | 5.9 | 10 |
 | |||
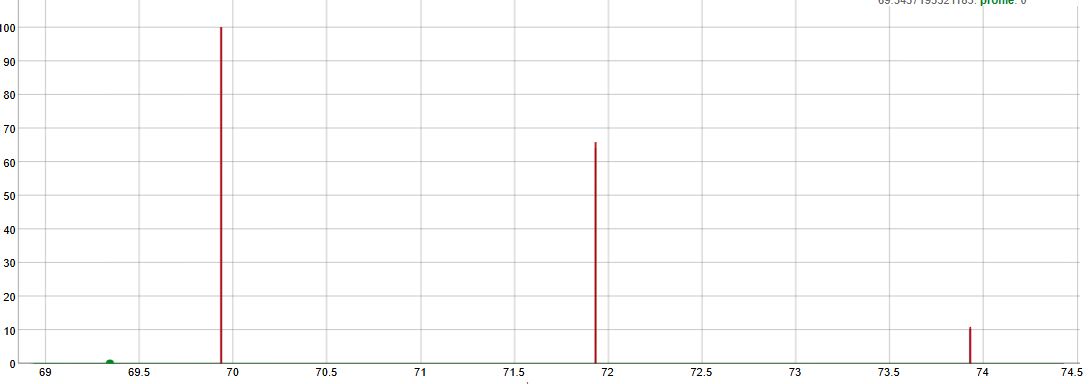
| (a + b)3 where a = percentage of 35Cl and b = percentage of 37Cl. | Intensities | ||
| 35Cl3 | m | a3 | 100 |
| 35Cl2 37Cl | m+2 | 3 a2 b | 98 |
| 35Cl 37Cl2 | m+4 | 3 a b2 | 32 |
| 37Cl3 | m+6 | b3 | 3 |
 | |||
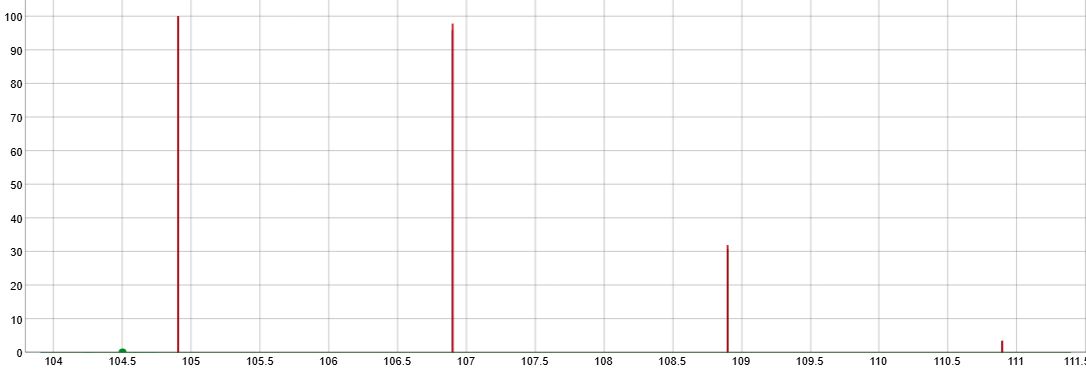
| (a + b)2 (c + d) where a = % of 35Cl, b = % of 37Cl, c= % of 79Br and d= % of 81Br. | Intensities | ||
| 35Cl2 79Br | m | a2 c | 60 |
| 2 35Cl 37Cl 79Br | m+2 | 2abc | 100 |
| 35Cl2 81Br | a2 d | ||
| 37Cl2 79Br | m+4 | b2 c | 46 |
| 2 35Cl 37Cl 81Br | 2 a b d | ||
| 37Cl2 81Br | m+6 | b2 d | 7 |
Intensity A1-Stable isotope (M+1)/(M)
Hereafter a quick approximation method to calculate the aggregated isotopic distribution.
Calculation for molecules containing CHNOPS
nC= nbre of carbon, nH= nbre of Hydrogen, nN=nbre of Nitrogen, nO= nbre of Oxygen, nS= nbre of Sulfur
Atoms involved in the case of M+1: 13C, 2H, 15N, 17O and 33S |
Intensity A2 -Stable isotope (M+2)/(M)
Atoms involved in the case of M+2: 18O ,34S, 37Cl, 81Br and 13C2, 2H2, 15N2, 17O2 ,33S2 Note that 17O and 2H are very rare. |
General method:
Total number of atoms = n (example if atom = carbon, for Fulleren C60 n=60)
Abundance of isotope =i (case of carbon,i for 12C = 0.989 and i for 13C =0.011)
Probability of x atoms = P (x) (for example: combination of one 13C or of two 13C)
| |
|